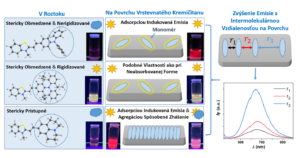
Influence of the structure of benzothiazole dyes on phenomena leading to changes in their luminescent properties
SiC ceramic materials with high thermal conductivity
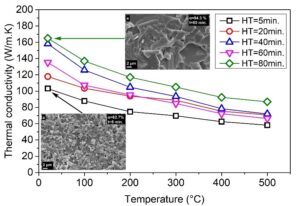
Fig. 1: Thermal conductivity of SiC ceramics depending on temperature and sintering time and therefore also on α-SiC content and grain size.
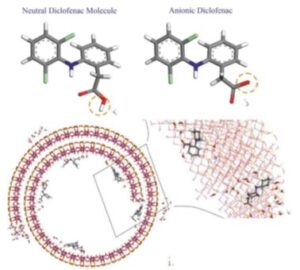
Stabilization of diclofenac by efficient binding on the halloysite surface
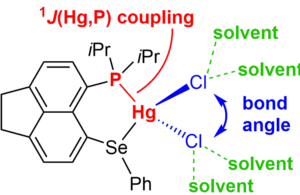
Investigation of the effect of solvation on 1J(Metal–P) spin–spin coupling
Formation of Polycrystalline YAG Channels via Femtosecond Laser in Microsphere-Sintered Glasses: Towards Erbium-Doped Waveguide Lasers
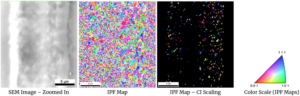
Fig. SEM and EBSD data from fs laser modification of the surface of YAG glass. Confidence index (CI) used as grayscales to remove glass background. EBSD, Electron backscatter diffraction.
The production of Al₂O₃–YAG–ZrO₂ via a straightforward single-step spark plasma sintering method
New strategies for joining high-entropic ceramics: from interface design to high-temperature joints
The Role of Dynamic Polyhedral Rotations in the Phase Transitions of Rb3AlF6 and Cs3AlF6
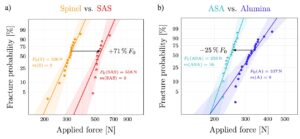
Mechanical properties of optical materials: Improving contact damage resistance by lamination
 Contact
Contact Intranet
Intranet SK
SK

